Unlocking the Future: Discover the Magic of SLA 3D Printing and Its Boundless Possibilities!
In recent years, the manufacturing landscape has been transformed by the advent of innovative technologies, with SLA 3D printing service at the forefront. Stereolithography, commonly known as SLA, has garnered significant interest for its ability to create intricate designs and prototypes with remarkable precision. This technology utilizes a process where liquid resin is cured layer by layer using ultraviolet (UV) light, allowing for the production of highly detailed objects that are often unattainable with traditional manufacturing methods. As industries continue to seek faster and more cost-effective solutions, understanding the significance of SLA 3D printing becomes paramount. This article will delve into the technology behind SLA printing, explore its diverse applications across various sectors, and speculate on its future advancements, illustrating why this method is considered a game changer in modern manufacturing.
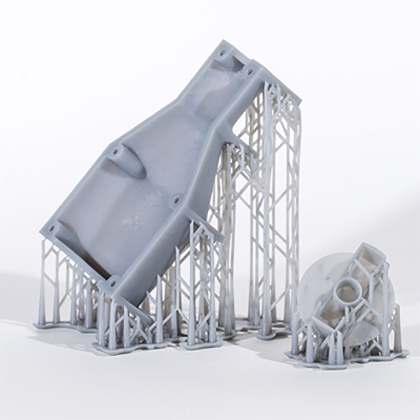

Understanding SLA 3D Printing Technology
SLA (Stereolithography Apparatus) is a pioneering 3D printing technology that revolutionized the manufacturing industry by introducing the concept of layer-by-layer construction of objects. The process begins with a vat of liquid photopolymer resin, which is sensitive to UV light. A UV laser is directed onto the surface of the resin, selectively curing the material and solidifying it into the desired shape. Each layer is built upon the last, allowing for intricate details and complex geometries to be achieved with ease. One of the key advantages of SLA over other 3D printing methods, such as FDM (Fused Deposition Modeling), is its ability to produce parts with exceptional surface finish and resolution. This is particularly advantageous for applications that demand high precision, such as dental molds or intricate jewelry designs. Furthermore, SLA technology is capable of producing functional prototypes that can be tested and iterated quickly, significantly reducing the time and cost associated with product development.
Applications of SLA 3D Printing in Various Industries
SLA 3D printing finds its applications across a myriad of industries, each benefiting from its unique capabilities. In the healthcare sector, for instance, SLA technology is employed to create customized implants and prosthetics tailored to individual patients. My friend, a biomedical engineer, once shared how they used SLA to produce a complex model that aided in surgical planning, allowing surgeons to visualize the procedure with greater clarity. The detailed medical models help in accurately simulating surgeries, which can lead to better outcomes. In the automotive industry, SLA is used for rapid prototyping of parts, enabling quicker design iterations and reducing time to market for new vehicles. Manufacturers can test and refine their designs promptly, ensuring that only the best products make it to production. Moreover, in aerospace, the lightweight and durable components produced through SLA can significantly enhance fuel efficiency and performance. Consumer products also benefit from SLA printing, where brands can create customized offerings that cater to consumer preferences, such as personalized phone cases or unique home decor items. The versatility of SLA technology empowers designers and engineers to push the boundaries of creativity and innovation.
Healthcare Innovations
Healthcare is perhaps one of the most promising fields for SLA 3D printing. The ability to create personalized medical devices and models is revolutionizing patient care. Customized implants are designed to fit the unique anatomy of each patient, enhancing comfort and effectiveness. Additionally, the precision of SLA printing allows for the production of intricate models that can be used for pre-surgical planning. These models provide surgeons with a tangible representation of the patient's anatomy, enabling them to strategize and rehearse complex procedures. The impact of this technology on patient outcomes cannot be overstated, as it leads to higher success rates and reduced recovery times.
Industrial Design and Prototyping
In the realm of industrial design, SLA printing serves as an invaluable tool for rapid prototyping. Designers can create high-fidelity prototypes that showcase the look and feel of the final product. This ability to iterate quickly and efficiently allows for an accelerated design process, ultimately shortening the time it takes to bring a product to market. Engineers can identify design flaws early in the process, saving both time and resources. The tactile feedback provided by SLA prototypes also enables stakeholders to engage more effectively in the design review process, leading to better-informed decisions and a more collaborative approach to product development.
The Future of SLA 3D Printing
The future of SLA 3D printing is bright, with numerous advancements on the horizon. Innovations in materials will enhance the range of applications for SLA technology, allowing for stronger, more durable, and even bio-compatible resins. Additionally, improvements in printing speed will further streamline the manufacturing process, enabling companies to produce parts at unprecedented rates. The integration of SLA printing with technologies like artificial intelligence (AI) and the Internet of Things (IoT) may also pave the way for smarter manufacturing processes, where machines can learn from data and optimize production in real-time. As sustainability becomes increasingly vital, SLA printing could contribute to more sustainable practices by reducing waste and enabling the production of lightweight components that require less energy during use. The potential impacts of these advancements are vast, promising to reshape the manufacturing landscape and redefine how we think about production.
Transformative Impact of SLA 3D Printing
In conclusion, SLA 3D printing is a transformative technology that is reshaping various industries by enabling the creation of highly detailed and customized products. From revolutionizing healthcare with personalized medical solutions to enhancing industrial design through rapid prototyping, the applications of SLA are vast and impactful. As we look to the future, the advancements in materials, speed, and integration with other technologies promise to unlock even more possibilities. It is an exciting time for those interested in exploring the capabilities of SLA 3D printing, and I encourage readers to consider its potential applications in their own fields or projects. Embracing this technology could lead to innovative solutions and a competitive edge in today’s fast-paced market.