Unlock Your Creativity: Discover the Secret to Perfect 3D Prints with PLA Filaments!
3D printing has revolutionized the way we think about design and manufacturing, opening up endless possibilities for creativity and innovation. One of the most crucial aspects of successful 3D printing is selecting the right filament, as it can significantly influence the quality and outcome of your projects. Among the myriad of materials available, PLA (Polylactic Acid) stands out as a favorite for both beginners and seasoned practitioners. Its user-friendly nature and environmentally friendly properties make it an ideal choice for a wide range of applications. In this article, we will guide you through the essential factors to consider when purchasing PLA filaments, ensuring you find the perfect fit for your next 3D printing adventure.
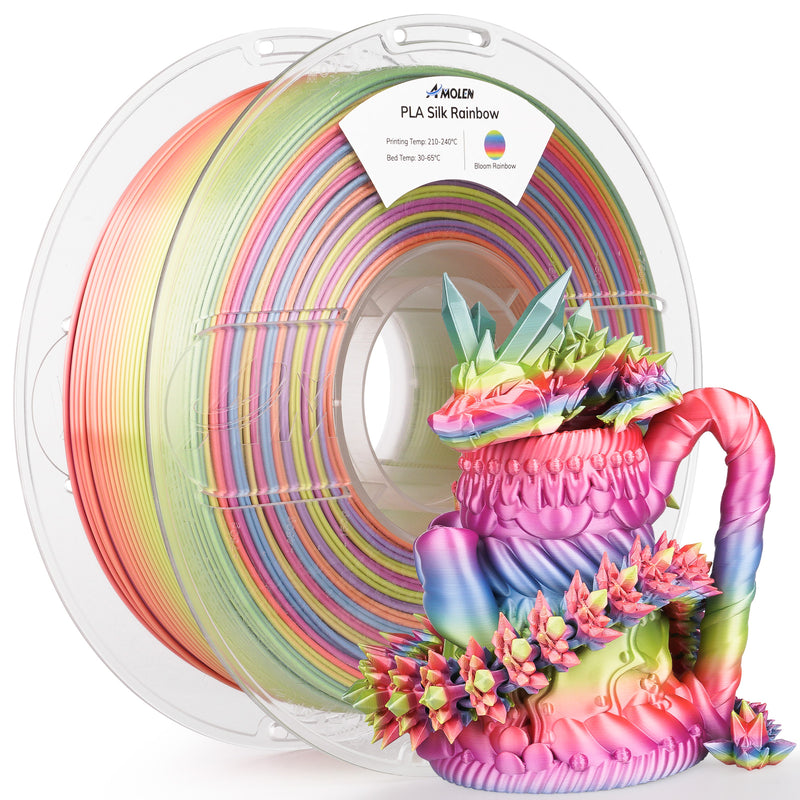

Understanding PLA Filaments
PLA, or Polylactic Acid, is a biodegradable thermoplastic derived from renewable resources like corn starch or sugarcane. One of its standout properties is its ability to print at lower temperatures compared to other plastics, making it a great option for those new to 3D printing. The ease of use is further enhanced by its minimal warping and excellent adhesion to the print bed, which results in high-quality prints with fine details. Another significant advantage of PLA is its eco-friendliness; being derived from natural sources, it is a more sustainable choice compared to petroleum-based plastics. This combination of user-friendliness, environmental benefits, and versatility makes PLA an attractive choice for various projects, from intricate models to prototypes.
Factors to Consider When Purchasing PLA Filaments
When it comes to buying PLA filaments, several key factors can influence your decision. First and foremost, the diameter of the filament is crucial, as most 3D printers are designed for either 1.75mm or 2.85mm filaments. Ensuring compatibility with your printer will save you a lot of hassle. Next, consider the color options available. PLA filaments come in a vast array of colors and finishes, including matte, glossy, and even translucent variants, allowing you to achieve the desired aesthetic for your prints. Additionally, the printability of different PLA brands can vary widely. Some may offer enhanced flow characteristics or improved finish, which can significantly affect the final output of your designs. A friend of mine once faced challenges with print quality because she chose a filament that wasn't optimal for her specific printer model. Learning from her experience, I emphasize the importance of researching and selecting the right filament for your setup.
Types of PLA Filaments Available
There are several types of PLA filaments available on the market, each designed to cater to different printing needs. Standard PLA is the most commonly used type, perfect for general-purpose printing. Then there's PLA+, which includes additives to enhance its strength, flexibility, and durability. This type is ideal if you're looking for more robust prints that can withstand wear and tear. Specialty blends, such as PLA infused with wood or metal particles, offer unique textures and appearances, perfect for artistic projects. These variations can significantly influence the outcome of your prints; for instance, a friend of mine once created stunning wood-look sculptures using wood-infused PLA, which added a charming touch to her home decor. Understanding the different types of PLA filaments will help you choose the best one for your specific applications.
Tips for Using PLA Filaments Effectively
To ensure successful 3D printing with PLA, it's essential to follow some practical tips. First, adjust the nozzle temperature to a range of 190°C to 220°C, as this will provide optimal flow and adhesion. Proper bed adhesion is also crucial; using a heated bed set to around 60°C can help prevent warping and ensure your prints stick during the process. Additionally, experimenting with different bed materials, such as blue painter's tape or glass, can significantly improve adhesion. After printing, consider post-processing techniques like sanding or applying a clear coat to enhance the finish of your projects. I've seen how these techniques can transform a simple print into a polished masterpiece, leaving a lasting impression on friends and family alike.
Maximizing Your 3D Printing Potential with PLA
In summary, selecting the right PLA filament is fundamental for achieving successful 3D printing results. By understanding the properties of PLA, considering important purchasing factors, exploring the various types available, and applying effective printing tips, you can unleash your creativity and bring your projects to life. Whether you're a beginner looking to create your first print or an experienced user seeking new challenges, PLA filaments offer a world of possibilities. So go ahead, experiment, and let your imagination guide your next 3D printing venture!