Unlock the Secrets: Why You Can't Afford to Ignore Residential Solar Systems!
As the world increasingly shifts towards sustainable energy solutions, residential solar systems have emerged as a pivotal element in this transformation. Not only do they provide homeowners with a way to reduce their electricity bills, but they also contribute to a greener planet by harnessing the power of the sun. The benefits of installing solar panels at home extend beyond cost savings; they include energy independence and a significant reduction in carbon footprint. This article aims to guide you through the process of comparing options and seeking quotes from various providers, ensuring you make an informed decision about investing in a residential solar system.
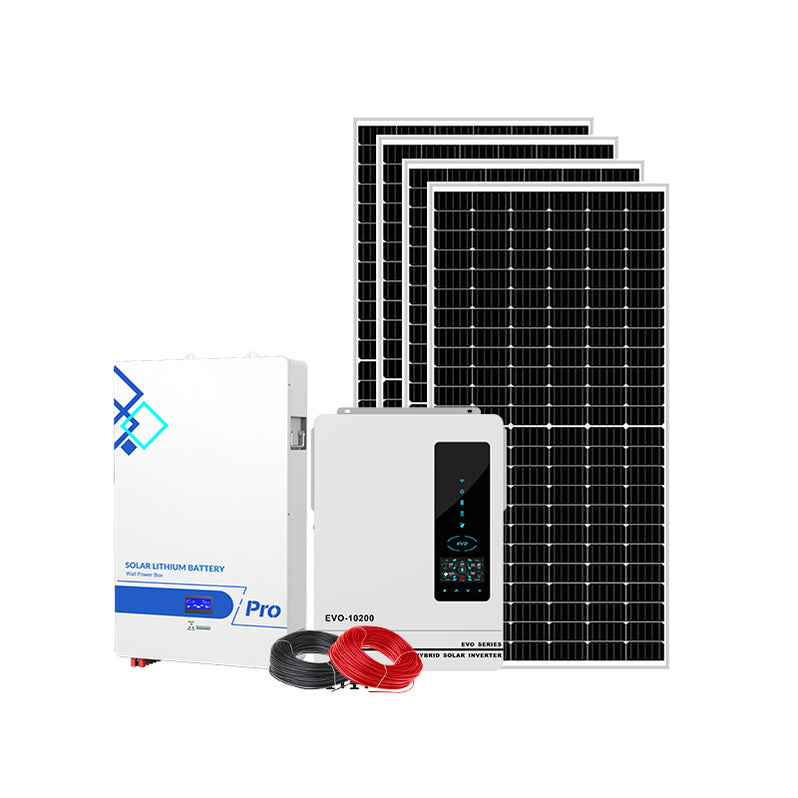

Understanding Residential Solar Systems
Residential solar systems are designed to capture sunlight and convert it into usable electricity for homes. The primary components of these systems include solar panels, inverters, and, in some cases, battery storage. Solar panels, usually installed on rooftops, consist of photovoltaic cells that convert sunlight into electricity. The inverter plays a crucial role by transforming the direct current (DC) generated by the panels into alternating current (AC), which is the form of electricity used in homes. Battery storage systems allow homeowners to store excess energy generated during sunny days for use during less sunny periods, providing an added layer of energy security. The key benefits of these systems include significant reductions in energy bills, increased property value, and the peace of mind that comes with using renewable energy.
Assessing Your Energy Needs
Before investing in a residential solar system, it's essential to evaluate your energy consumption and needs. Start by examining your electricity bills to understand your average monthly usage. This information will help determine the size of the solar system you need. For instance, a household with high energy consumption may require a more extensive system compared to one with lower usage. Additionally, consider your future energy needs, such as plans for home expansions or the addition of electric vehicles. This assessment is crucial, as it ensures that the solar system you choose will adequately meet your household's energy demands now and in the future.
Comparing Solar Providers
When it comes to selecting a solar provider, thorough research is essential. Start by looking into the reputation of different companies—read customer reviews, check their ratings with consumer protection agencies, and seek recommendations from friends or family who have recently installed solar systems. Customer service is another critical aspect; you want a provider that is responsive and helpful, especially during the installation process. Additionally, inquire about the installation practices they use and the warranties they offer on their systems. Obtaining multiple quotes from various providers can also help you gain a clearer understanding of the market, allowing you to make a more informed decision. This competitive approach can lead to better pricing and service options.
Cost Considerations and Financing Options
Generally, the cost of residential solar systems can vary widely based on factors such as system size and installation complexity. While specific price points are not discussed here, it's essential to explore the various financing options available to homeowners. Traditional loans, solar leases, and power purchase agreements (PPAs) are common methods for financing a solar system. In many regions, government incentives and tax credits can significantly reduce the overall cost of installation. Although the initial investment might be substantial, the long-term savings on electricity bills and the potential increase in home value often provide a strong return on investment, making solar energy a financially sound choice.
Making the Final Decision
As you approach the final decision regarding the purchase of a residential solar system, it's vital to weigh all the factors discussed. Consider not only the upfront costs but also the long-term benefits such as energy savings, environmental impact, and energy independence. Take your time to compare quotes and providers, ensuring that you choose an option that aligns with your energy needs and financial situation. Remember, investing in solar energy is not just a financial decision—it's a commitment to a sustainable future.
Empowering Your Decision for a Sustainable Future
In conclusion, residential solar systems represent a significant opportunity for homeowners looking to reduce their energy costs while contributing to a cleaner environment. The advantages of investing in solar energy are manifold, from economic benefits to ecological ones. As you navigate the process of seeking quotes and comparing options, remember to consider your unique energy needs and the long-term implications of your investment. Don't overlook the transformative power of solar energy—taking the next steps could lead to a brighter, more sustainable future for you and your family.